Oatmeal Production process and operation methods
Process flow: Bare oats → Cleaning → Crushing → Cleaning → Drying → Microwave enzyme inactivation heat treatment → Granulation → Steaming → Pressing → Microwave drying → Cooling → Packaging → Finished product
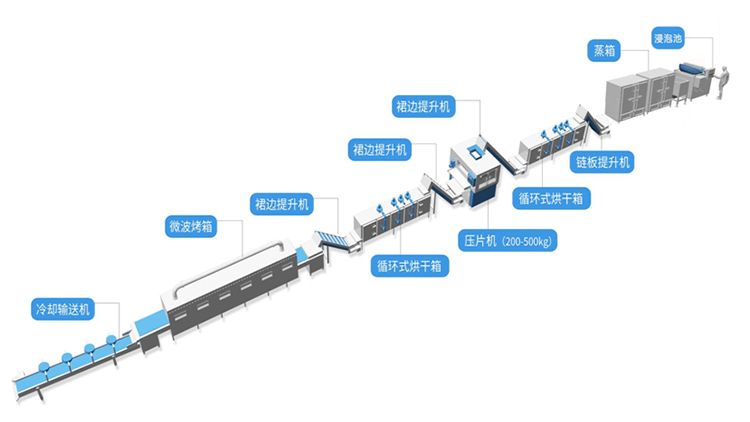
Operation method
1. Cleaning: The cleaning process of oats is similar to that of wheat. Generally, clean oats can only be obtained after multiple cleaning steps based on differences in particle size and specific gravity. The commonly used equipment includes initial cleaning machine, vibrating screen, peeling machine, iron remover, rotary screen, specific gravity screen, etc.
2. Skin milling and whitening: From the perspective of health care, oat bran is the essence of oats. Because a large amount of soluble fiber and fat are in the bran layer, the purpose of skin milling is to whiten and remove dust. The peeling of oats only requires gentle friction to remove the wheat wool and skin, and cannot be done too much like rice husking.
3. Cleaning and drying: After peeling, clean thoroughly and then centrifuge and dry.
4. Enzyme inactivation heat treatment: Oats contain various enzymes, especially lipoxygenase. If enzyme inactivation treatment is not carried out, the fat in oats will be promoted to oxidation during processing, affecting yield, quality, and shelf life. Heating treatment can inactivate enzymes, gelatinize oat starch, and enhance baking aroma. Generally, microwave heating equipment can be used. The oats after heating treatment must be promptly processed in the next process or forced to cool in a timely manner. Prevent the oil in oats from overheating and oxidation.
5. Granulation: Oatmeal is available in both whole grain and pellet compression forms. Granulation is the process of cutting oats into 1/2 to 1/3 sized particles using a rotary granulator. The oat flakes are uniformly shaped and easily compressed into thin sheets without forming powder.
6. Steaming: Its purpose is threefold: firstly, to further inactivate enzymes and sterilize oats; The second is to fully gelatinize the starch to meet the requirements of ready to eat or fast cooking; The third is to make oats smooth and soft, making them easy to compress into tablets. Steaming equipment uses a reversible steaming machine.
7. Pressing: Oats that have been steamed and moistened are pressed into thin sheets using a double roll press, with a thickness controlled at around 0.5 millimeters. If the thickness is too thick, the cooking time will be long, and if it is too thin, the product will be fragile. It is better for the roller diameter of the tablet press to be larger, usually around 200 millimeters.
8. Drying and cooling: Oats that have been compressed need to be dried to reduce their moisture content to below 10% for better preservation. Oatmeal is relatively thin and has a large contact area. When drying, a little hot air or even just cold air can achieve the purpose of drying. The drying equipment selected is the microwave drying sterilizer produced by Shandong Kehong Microwave Energy Co., Ltd. After drying, cool to room temperature.
9. Packaging: Generally, materials with good air tightness are used, such as aluminum plated film, polypropylene bags, and polyester bags. In addition, oatmeal is a fast food with high hygiene requirements, and the later stages of steaming and cooking should strive for aseptic production within the system.




